Why Class 6 & 9 DG Shipments from Qingdao to Egypt Require 14-Day Advance Booking
In DG logistics, speed becomes the enemy of safety and compliance. Class 6 toxic substances and Class 9 miscellaneous dangerous goods face multiple verification layers that cannot be compressed.
The Qingdao to Egypt route compounds this challenge by combining Chinese Maritime Safety Administration strictness with Egyptian Advanced Cargo Information system complexity.
Class 6 and 9 cargo consistently gets rejected when shippers apply general cargo booking timelines. The 14-day advance booking rule is not a suggestion but the minimum timeline to satisfy Chinese MSA verification, Shanghai carrier technical approval, and Egyptian ACI compliance. These three processes operate sequentially, not simultaneously.
This article explains why timing errors cause DG rejections and how to structure your documentation timeline correctly:
Why Shanghai headquarters controls all carrier approvals
How MSA declaration cut-offs differ from general cargo deadlines
What Egyptian Customs specifically requires for Class 6 toxic substances
How to structure your documentation and timeline to prevent costly rejections
China DG Export Regulations: MSA and IMDG Code Requirements
Every dangerous goods shipment from China undergoes a two-tier verification system mandated by the IMDG Code and China's Decree 591 (Regulation on the Safe Management of Hazardous Chemicals). This dual framework ensures that both international maritime standards and Chinese domestic safety regulations are satisfied before cargo leaves port.
Documentation Requirements by DG Class
For All DG Cargo:
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) with English translation
Performance Certificate for Dangerous Goods Packaging (危包证)
Certificate for Safe Transport of Chemical Goods
UN marking validation
For Class 6 Toxic Substances:
LD50/LC50 values verification and test reports
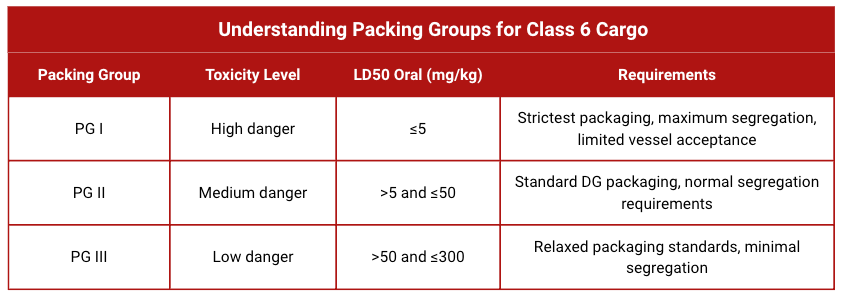
Packing Group determination (PG I, II, or III) based on toxicity levels
Acid/Chemical Analysis Report
Enhanced segregation documentation
For Class 9 Miscellaneous (especially UN 3077/3082):
Environmentally hazardous substances certification
Marine pollutant marking documentation
Environmental impact assessments
Special handling instructions
The difference between packing groups affects which vessels will accept your cargo and where it can be stowed. PG I substances face the most restrictive shipping conditions.
Qingdao MSA's Zero-Tolerance Enforcement
Qingdao MSA enforces packaging standards with zero tolerance for discrepancies:
UN markings on drums must match packaging certificates exactly
Certificate shows "UN 1A2/Y150/S" but drum displays "UN 1A2/Y145/S"? Rejected.
No relationships or expedite fees change enforcement
Cargo will not pass warehouse gate with any marking mismatch
Port authorities reject shipments for marking mismatches that other ports might overlook. This enforcement reality makes pre-shipment documentation audit essential.
Why All Qingdao DG Bookings Go Through Shanghai (3-5 Day Approval)
When you submit a DG booking in Qingdao, you interact with the local carrier office. That interaction represents only the preliminary stage of approval. Major carriers including Maersk, CMA CGM, and COSCO centralize all Asia-Pacific dangerous goods approvals at their Shanghai headquarters. Qingdao offices lack the authority to approve DG bookings independently.
The Two-Stage Approval Process
Stage 1: Qingdao Local Office (Initial Check)
Basic documentation completeness review
Preliminary HS code verification
Booking request forwarded to Shanghai
Obvious gaps result in immediate rejection without Shanghai review
Stage 2: Shanghai DG Desk (Technical Approval - 3-5 Working Days)
Cross-check cargo against vessel's Document of Compliance (DoC)
SOLAS Convention stowage limitation analysis
IMDG Segregation Table compatibility verification
Vessel capacity and "hot spot" availability check
What Shanghai Actually Evaluates
Vessel Capacity Constraints:
On-deck vs. under-deck stowage limitations
Each vessel has specific "hot spots" for different DG classes
If designated areas are full, booking gets rejected
Physical space availability does not guarantee DG acceptance
Segregation Requirements (IMDG Code Segregation Table):
Class 6 toxic substances cannot be near Class 8 corrosives
Incompatible DG cargo already loaded results in automatic rejection
Example: Class 6 toxic liquid rejected because vessel already carries Class 8 acids in adjacent bay
Segregation requirement is absolute with no exceptions
Stowage Plan Conflicts:
Vessels finalize stowage plans 7-10 days before departure
Plans account for weight distribution, stability, and segregation
Late DG bookings disrupt pre-approved calculations
Shanghai must recalculate vessel stability for any additions
Why Booking Rejections Happen
Common rejection reasons include:
Contract priority: Long-term customers receive DG capacity allocation first
Class-specific limits: Vessel's Document of Compliance restricts certain UN numbers
Hot spot capacity: Designated DG storage areas already at maximum
Segregation conflicts: Incompatible cargo already booked
Late submission: Stowage plan already finalized, cannot accommodate changes
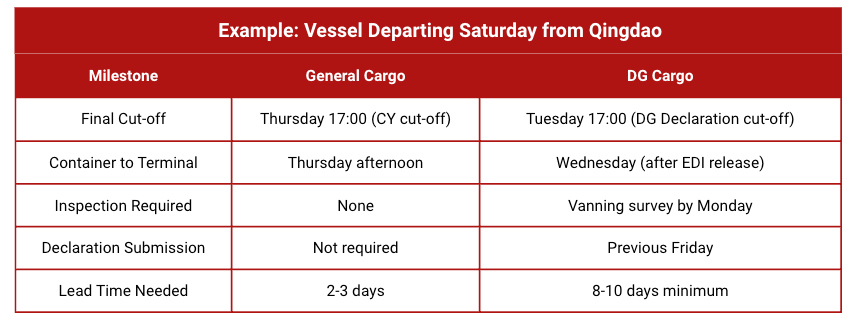
DG Declaration Cut-off vs. CY Cut-off: The 48-72 Hour Gap
General cargo shippers target the CY cut-off, the deadline when containers must arrive at the terminal for loading. DG cargo operates under a different deadline called the DG Declaration cut-off, which occurs 48-72 hours earlier than the vessel's CY cut-off.
Timeline Comparison: General vs. DG Cargo
Example: Vessel Departing Saturday from Qingdao
Missing the DG declaration window results in automatic short-shipment even if your container physically arrives at the terminal on time.
The Complete DG Shipping Process
Step 1: Draft Declaration Submission
Electronic data submission to MSA system
All technical specifications must be accurate
Errors trigger rejection and force complete resubmission (2-3 day delay)
System validates UN numbers, packing groups, and certificate compatibility
Step 2: Vanning Survey
A third-party surveyor must witness container stuffing and verify:
Cargo properly braced and secured to prevent shifting
Class 6/9 labels (placards) correctly displayed on all four sides
UN markings visible and compliant with specifications
No damaged packaging or leaking containers
Proper container condition before loading
The survey report is mandatory for MSA approval. No survey report means no EDI release.
Step 3: MSA Approval and EDI Release
MSA reviews draft declaration and survey report together
Upon approval, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) release issued
Only with EDI can container enter terminal's designated DG area
Terminals maintain separate DG areas with specialized safety systems
Consequences of Missing DG Declaration Cut-off
If you miss the deadline, you face:
Demurrage: $100-200/day (container sitting at terminal beyond free time)
Detention: $100-200/day (container exceeding equipment rental period)
Rebooking Fees: $150-300 (securing space on next vessel)
ACI Re-filing: $100-200 (Egyptian customs documentation for new vessel)
Storage at DG Area: $50-100/day (terminal charges for DG cargo holding)
Total Typical Cost: $2,000-3,000+ (plus lost sales from delivery delays)
The carrier will short-ship your container, leaving it at the terminal while the vessel departs without it.
Egypt ACI Requirements for Class 6 & 9 DG Imports
Egypt's Advanced Cargo Information system requires mandatory pre-arrival electronic filing for all cargo entering Alexandria and Sokhna ports. The ACI must be submitted before your vessel departs China. Late submissions or filing after departure result in cargo being held at transshipment ports like Jeddah or Port Said until documentation corrections are made.
Egyptian Customs Requirements for Class 6 Toxic Substances
Standard DG Documentation:
MSDS with English and Arabic translation
UN Packaging Performance Certificate
Certificate for Safe Transport of Chemical Goods
Commercial invoice and packing list
Class 6 Specific Requirements:
LD50/LC50 Test Reports: Verify toxicity classification (included in booking documentation)
Acid/Chemical Analysis Report: Detail exact chemical composition (3-5 days to obtain)
Chamber of Commerce Legalization: Authenticate documents for high-toxicity substances (3-5 business days)
Consignee Import License: Verify legal authority to import chemicals (validated before release)
Health Certificate: Required for public health impact substances (5-7 days from Chinese authorities)
Enhanced Scrutiny Triggers:
Class 6 Division 6.1 (toxic substances) face automatic detailed inspection
LD50/LC50 values below certain thresholds trigger health ministry review
First-time importers experience 30-50% longer clearance times
Repeat importers with good compliance history receive faster processing
The Critical Data Consistency Rule
Your Chinese DG Declaration must match your Egypt ACI filing exactly across all data points:
Required Data Match:
UN number identical in both systems
Packing group classification (PG I, II, III) consistent
Net weight matches exactly (no rounding differences)
Gross weight matches exactly
HS code aligns between Chinese export and Egyptian import
Chemical name spelling identical in both English documents
Consequences of Data Mismatch:
Immediate Impact:
Cargo stuck at transshipment ports (Jeddah, Port Said, Jebel Ali)
Egyptian Customs rejects entry authorization
No resolution possible once cargo is in transit
Financial Consequences:
Transshipment port storage: $50-150/day
Potential re-export to China: $3,000-5,000
Cargo destruction if deemed non-compliant: Total loss
Importer's future shipments face enhanced scrutiny
Operational Impact:
Cannot access cargo to verify information
Cannot correct declarations remotely
Forced to accept full loss or pay re-export costs
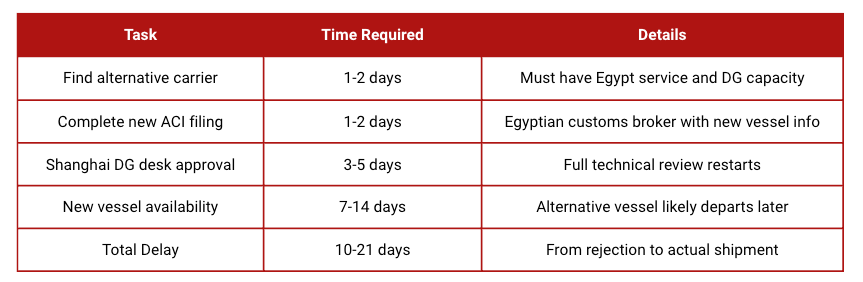
Backup Plan Timeline
If your primary carrier rejects the DG booking, expect this timeline:
This delay explains why the 14-day advance booking rule includes buffer time for carrier rejections.
How to Prepare Class 6 & 9 DG Shipments: 14-Day Timeline and Critical Rules
The 14-day timeline represents the minimum period required to satisfy all regulatory checkpoints between booking request and vessel departure. Each phase addresses specific requirements that cannot be rushed or skipped.
14-Day Preparation Timeline
The 14-day timeline represents the minimum period required to satisfy all regulatory checkpoints between booking request and vessel departure. Each phase addresses specific requirements that cannot be rushed or skipped.
Days 1-3: Documentation Pre-Audit
Verify MSDS accuracy and completeness
Confirm UN packaging certificates match drum markings exactly
Determine correct packing group for Class 6 cargo (based on LD50/LC50 data)
Identify segregation requirements using IMDG Segregation Table
Prepare Egypt-specific documentation (Analysis Report, Chamber of Commerce legalization)
Critical output: Complete documentation package ready for submission
Days 4-7: Carrier Booking and Shanghai Approval
Submit booking with complete technical data to carrier DG desk
Shanghai DG desk conducts technical review (vessel capacity, segregation, DoC compliance)
Verify vessel stowage capacity and compatibility with existing cargo
Receive booking confirmation or rejection notification
If rejected, immediately pursue alternative carrier
Critical output: Confirmed booking with approved vessel
Days 8-10: MSA DG Declaration Preparation
Submit draft declaration to MSA electronic system
Prepare Certificate for Safe Transport of Chemical Goods
Coordinate with Egyptian customs broker to begin ACI filing
Schedule third-party vanning survey with adequate notice
Critical output: MSA draft declaration accepted, survey scheduled
Days 11-12: Vanning Survey Execution
Third-party surveyor witnesses container stuffing at your facility
Verify cargo bracing, labeling compliance, and UN marking accuracy
Obtain official vanning survey report
Submit survey report to MSA along with draft declaration
Critical output: Vanning survey report completed and submitted
Days 13-14: Final Approval and Terminal Delivery
MSA issues EDI release authorization
Container delivered to terminal's designated DG area
Egypt ACI filing confirmed with customs broker
Cargo ready for vessel loading
Critical output: Container in terminal DG area with all approvals complete
Buffer Time Requirements
Built into the 14-day timeline are buffers for predictable delays:
Documentation corrections: 2-3 days when MSA identifies errors
Alternative carrier booking: 5-7 days if primary carrier rejects
ACI filing complications: 1-2 days for data validation failures
Attempting to compress this timeline guarantees failure because regulatory processes operate on fixed schedules.
Three Critical Rules for DG Shippers
Rule 1: Prepare Your Documents 15 Days Ahead
Complete documentation must be ready before you contact any freight forwarder. Missing a single document adds 3-5 days to your timeline.
Required Documentation Package:
MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet): Complete safety data with English translation (should already exist from manufacturer)
UN Packaging Performance Certificate: Must match drum markings exactly (obtain from packaging supplier)
LD50/LC50 Test Reports: For Class 6 packing group determination (allow 7-10 days if testing needed)
Egypt ACI Reference Number: Customs broker contact or ACI number (arrange customs broker immediately)
Certificate for Safe Transport of Chemical Goods: Chinese export requirement (3-5 days from qualified lab)
Acid/Chemical Analysis Report: Egypt requirement for Class 6 toxic substances (5-7 days from certified lab)
Chamber of Commerce Legalization: If required for high-toxicity substances (3-5 business days)
The 14-day booking window assumes documentation completeness from day one. Discovering missing certificates on day 5 pushes your entire schedule beyond the viable booking window.
Rule 2: Never Misdeclare DG as General Cargo
Some shippers attempt to hide dangerous goods classification to bypass DG procedures and accelerate shipping. This represents criminal activity under Chinese law, not a time-saving strategy.
Chinese Penalties for DG Misdeclaration:
Fines up to RMB 300,000 per shipment
Criminal liability for company legal representatives (potential imprisonment)
Permanent carrier blacklisting (prevents all future bookings)
MSA export ban (prohibits DG shipments from any Chinese port)
Company reputation damage in freight community
Egyptian Consequences:
Egyptian Customs conduct random X-ray inspections on arriving containers. Undeclared DG discovered at Alexandria or Sokhna results in:
Immediate cargo confiscation
Substantial fines under Egyptian hazardous materials laws
Criminal prosecution for repeated violations or particularly dangerous misdeclarations
Importer's future shipments subject to 100% inspection rate
The cost of proper DG handling represents a small fraction of misdeclaration consequences. Legal compliance protects both your immediate shipment and your long-term ability to import from China.
Rule 3: Choose a Freight Forwarder Who Speaks Technical Language
Not all freight forwarders understand dangerous goods logistics. Your forwarder's technical competence determines whether your shipment succeeds or fails.
Essential Questions Your Forwarder Must Answer:
What is the packing group (PG I, II, or III) of my Class 6 cargo based on the LD50 values in my test report?
How does the Shanghai DG desk approval process work for my specific carrier?
What are the IMDG Code segregation requirements between my cargo and other DG classes commonly shipped to Egypt?
How do you coordinate Chinese DG declaration data with Egypt ACI filing to prevent mismatches?
What is your process for handling vanning surveys and MSA EDI releases?
Red Flags Indicating Insufficient Expertise:
Generic answers: "We handle all documentation" or "Don't worry, we'll take care of it"
Cannot explain packing group determination process
Unfamiliar with Shanghai approval timeline specifics
No mention of segregation requirements
Promises booking within 3-5 days for new DG cargo
Does not ask technical questions about your cargo
At Gerudo Logistics, we start every Qingdao-Egypt DG inquiry with technical questions about packing groups, segregation requirements, and MSA compliance timelines. Our operations team maintains direct communication with Shanghai DG desks at major carriers and coordinates Chinese DG declarations with Egypt ACI filings simultaneously using identical data sets.
We do not manage DG shipments. We engineer compliance pathways that prevent rejections before they happen.
DG logistics requires precision in classification, documentation, and regulatory compliance. Vague reassurances suggest your forwarder lacks the expertise to navigate the specific technical requirements that govern Class 6 and Class 9 shipments.
Class 6 & 9 DG Shipping to Egypt: Frequently Asked Questions
Why can't I book Class 6/9 DG cargo one week before the vessel like general cargo?
DG cargo requires Shanghai approval (3-5 days), MSA declaration and vanning survey (3-4 days), and Egypt ACI filing (2-3 days). These processes are sequential and cannot be compressed.
What happens if the Shanghai DG desk rejects my booking?
You must find an alternative vessel with DG capacity, restarting the approval process. This adds 7-10 days minimum. New Egypt ACI filing is required if vessel routing changes.
Can I pay expedite fees to speed up MSA approval?
No. MSA follows strict regulatory timelines. Approval depends entirely on documentation completeness and accuracy, not payment.
What specific documents does Egyptian Customs require for Class 6 toxic substances?
MSDS with English and Arabic translation, LD50/LC50 test reports, Acid/Chemical Analysis Report, Certificate for Safe Transport, and Chamber of Commerce legalization if substance exceeds toxicity thresholds.
How do I prevent ACI data mismatch between China DG declaration and Egypt filing?
Work with a forwarder who coordinates both filings simultaneously using identical data sets. Request copies of both declarations before vessel departure to verify all data matches.
What are the real costs if my DG cargo misses the vessel?
Demurrage and detention ($100-200/day), rebooking fees ($150-300), terminal storage ($50-100/day), and ACI re-filing ($100-200). Total typically exceeds $2,000-5,000 per missed vessel.
Can I switch carriers mid-process if the first one rejects my booking?
Yes, but you lose all approval progress. The new carrier requires fresh Shanghai approval, new MSA declaration, and new Egypt ACI filing if routing differs.
Conclusion
Shipping Class 6 and Class 9 dangerous goods from Qingdao to Egypt requires risk mitigation through regulatory compliance at every stage. The process extends beyond moving cargo from origin to destination.
The 14-day advance booking rule exists because Chinese MSA requirements, Shanghai carrier approval processes, and Egyptian ACI compliance cannot be compressed without creating safety risks and legal violations. Each regulatory checkpoint serves specific purposes in ensuring that toxic substances and environmentally hazardous materials move safely through international supply chains.
Success in DG logistics demands three elements:
Complete technical documentation prepared before booking requests
Accurate regulatory knowledge of both Chinese export and Egyptian import requirements
Sufficient timeline for multi-party approvals with buffer for predictable delays
If you have Class 6 or Class 9 cargo for Egypt, prepare your documentation 15 days before your desired vessel departure. Contact Gerudo Logistics for pre-shipment documentation audits and Qingdao-Egypt DG route compliance consultation.