Customs Clearance for Reefer Containers from China: Documents, Compliance & Costs Explained
When you're moving perishable cargo across borders, customs clearance isn't just about tariffs and paperwork. It's about time, temperature integrity, and regulatory precision working together in a narrow window. Your cargo counts down from the moment it's loaded, every hour of delay costs you shelf life, and unlike dry containers, your reefer needs continuous power, monitoring, and rapid movement through checkpoints.
The complexity multiplies when you factor in health certificates, phytosanitary inspections, pre-arrival notifications, and destination-specific licensing requirements. This guide walks you through the complete customs clearance process for reefer containers from China, covering documents, compliance steps, and cost structures.
Just getting started with international cold chain? Explore our ultimate guide to reefer container shipping from China.
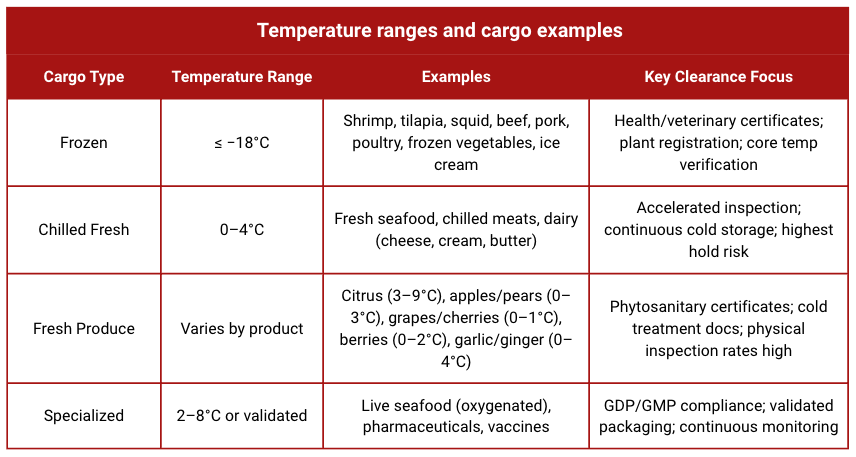
Understanding Reefer Cargo Types and Temperature Requirements
Your clearance complexity depends on what you're shipping. Different cargo types face different regulatory scrutiny and temperature tolerances.
Frozen cargo offers longer shelf life during delays but faces stricter origin controls. Chilled cargo has tight time windows and premium processing fees. Fresh produce requires phytosanitary compliance and ventilation management.
Full Document Checklist for Reefer Customs Clearance
Exporter-Side Documents (China Origin)
Commercial Invoice – HS codes, declared value, Incoterm, product description, quantity, processing method, production date/batch code
Packing List – Container number, seal, gross/net weight, carton count, stowage pattern
Bill of Lading (B/L) – Shipper, consignee, ports, container type, temperature set-point
China Export Declaration – Filed through Single Window system; must match invoice and packing list
Health/Veterinary Certificate – For animal products (meat, seafood, dairy); issued by GACC; certifies plant registration and product safety
Phytosanitary Certificate – For plant products; issued by GACC; proves pest-free status
Certificate of Origin – RCEP, Form E (ASEAN-China FTA), or standard; enables preferential tariffs
Pre-Trip Inspection (PTI) Record – Proves reefer unit tested before loading; critical for dispute resolution
Temperature Data Logger Report – Electronic log tracking temperature throughout transit; expected by customs and insurers
Cold Treatment Certificate – Required for certain fruits (citrus, grapes) to specific markets
Importer-Side Documents (Destination Country)
Import License/Permit – Many countries restrict food imports to licensed entities covering specific product categories
Pre-Arrival Notification Filings – Varies by destination (detailed in regional compliance section)
Laboratory Certificates – Residue testing, microbiological analysis, or nutritional verification as required
Labeling Compliance Documentation – Ingredient lists, allergen warnings, nutrition facts in destination language/format
Insurance Certificate – Marine cargo insurance covering temperature deviation losses
Purchase Order/Sales Contract – Transaction verification for customs
China Export-Side Compliance: What Happens Before Your Container Leaves
Exporter Registration and Plant Approval
For animal products (meat, seafood, dairy), the Chinese processing facility must be GACC-registered and approved for export to your destination market. Check official establishment lists before signing contracts.
CIQ/GACC Inspection and Export Declaration
High-risk products undergo origin inspection. GACC verifies plant conditions, product samples for residues, temperature records, batch traceability, and container loading. Inspections take 1–3 business days.
Every export requires electronic customs declaration through China's Single Window. The declaration includes accurate HS code, FOB value, quantity, destination, and transport information. Shipping lines require proof of export clearance before releasing the B/L.
PTI and Container Loading
Conduct Pre-Trip Inspection before loading: verify compressor function, temperature probe accuracy, airflow patterns, stable set-point, and no contamination. Install a calibrated temperature data logger positioned per manufacturer instructions.
Document your set-point, ventilation settings, and loading pattern. Frozen cargo typically runs at −18°C with minimal ventilation; fresh produce requires specific vent rates and humidity control.
Incoterm Responsibilities
FOB/CFR/CIF: Seller manages China export clearance
EXW: Buyer arranges export clearance (often via Chinese forwarder)
FCA: Depends on named place
Clarify responsibilities in writing before production.
Destination Import Compliance: Regional Requirements
Once your reefer container arrives, new compliance rules take effect. While all destinations share a common inspection framework, each region adds unique requirements.
Universal Import Process (All Markets)
Regardless of destination, expect these three core steps:
Pre-Registration/Licensing – Importer must hold valid licenses covering the product category; processing plants often require destination-market approval before first shipment
Port Inspection – Documentary review, identity checks, and physical examination (frequency varies by product risk level and market)
Laboratory Testing – Sample analysis for residues, microbiological parameters, or quality verification (routine or risk-based depending on jurisdiction)
Below are the unique requirements each market adds to this universal framework.
United States
Pre-Arrival Filing: ISF 10+2 (24 hours before loading at Chinese port); FDA Prior Notice (before vessel arrival)
Primary Authorities: FDA (Food and Drug Administration), USDA FSIS (meat/poultry), CBP (Customs and Border Protection)
Unique Requirements: FSIS plant approval mandatory for meat and poultry exports; cold treatment verification required for certain fruits (citrus, grapes, lychee); antidumping and countervailing duties (ADD/CVD) commonly applied to frozen seafood
Timeline: ISF must be filed 24 hours pre-loading; Prior Notice before arrival
European Union
Pre-Arrival Filing: TRACES NT system (CHED-P for products of animal origin, minimum 24 hours before arrival)
Primary Authorities: EU Commission, Member State Border Control Posts (BCPs)
Unique Requirements: Entry only through designated BCPs with veterinary inspection capacity; RASFF (Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed) alert history triggers increased scrutiny; all POAO undergo documentary, identity, and physical checks
Timeline: CHED-P notification at least 24 hours pre-arrival
Middle East (UAE, Saudi Arabia)
Pre-Arrival Filing: Embassy-legalized certificates required 1–2 weeks before shipment
Primary Authorities: SFDA (Saudi Food and Drug Authority), MOCCAE (UAE Ministry of Climate Change and Environment)
Unique Requirements: Halal certification mandatory for meat, poultry, and many processed foods; product registration with SFDA required before import to Saudi Arabia; health and phytosanitary certificates must be legalized through Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs and destination country embassy
Timeline: Certificate legalization takes 1–2 weeks; product registration varies by category
Latin America (Brazil, Mexico, Chile)
Pre-Arrival Filing: Dichave/import license (Brazil, before shipment); Avisos permits (Mexico, before arrival); SAG authorization (Chile, advance approval)
Primary Authorities: MAPA (Brazil Ministry of Agriculture), SENASICA (Mexico), SAG (Chile Agricultural and Livestock Service)
Unique Requirements: Plant-specific approval lists maintained by Brazil MAPA and Chile SAG, only approved Chinese facilities can export; Mexico conducts physical inspections at 40–60% rate; shelf-life validation against transit time commonly verified; some countries require Spanish-language labels
Timeline: Import permits typically require 1–4 weeks advance application
India
Pre-Arrival Filing: Import declaration with IEC (Import Export Code) and FSSAI license covering product category
Primary Authorities: FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), Plant Quarantine
Unique Requirements: Embassy endorsement often required for health certificates from China; frequent laboratory testing even when origin certificates are provided; FSSAI product approval and importer registration must be in place before first shipment; additional state-level registrations may apply
Timeline: FSSAI registration is ongoing requirement; standard entry procedures at port
Indonesia
Pre-Arrival Filing: BPOM product registration (requires 3–6 months for new products)
Primary Authorities: BPOM (National Agency of Drug and Food Control), Agricultural Quarantine Agency
Unique Requirements: Mandatory product registration with BPOM before first import, plan 3–6 months ahead for new products; health certificates require Indonesian embassy endorsement in China; Halal certification (MUI-recognized) mandatory for meat, poultry, and most processed foods; quarantine inspection at all entry points
Timeline: BPOM registration 3–6 months; quarantine clearance at entry
Cost Breakdown: Where Importers Overpay on Reefer Clearance
Reefer clearance costs extend well beyond customs duties.
Port and Terminal Charges
Plug-In Fees: $50–150/day for electricity and temperature monitoring
Cold Storage: $300–800/container/day during inspection holds
Reefer Inspection Fees: $200–500/inspection due to handling complexity
Demurrage and Detention: $150–300/day (reefer); starts after 5–7 free days
Customs and Compliance Costs
Customs Duties: Varies by HS code; seafood often 0–6%; produce varies widely; processed foods 10–20%. Add VAT/GST in applicable markets.
Brokerage Fees: $150–400/entry; premium for expedited reefer processing
Health/Phytosanitary Inspection Fees: Government charges for physical inspections and lab testing
Certificate Fees: $50–200/document from Chinese authorities
HS Code Classification Impact on Costs
Accurate HS classification directly affects duty rates and compliance requirements. For example:
Frozen Shrimp: HS 0306.17 typically carries lower duty but faces antidumping duties in US market
Fresh Citrus: HS 0805.10–0805.50 ranges trigger different phytosanitary requirements and seasonal quotas
Frozen Vegetables: HS 0710.xx generally faces lower scrutiny but requires accurate variety classification
Dairy Products: HS 0406.xx (cheese) faces import quotas and licensing in many markets
Misclassification leads to re-liquidation penalties, delayed clearance, or rejected entries. Invest in expert classification before your first shipment.
Where Importers Overpay
Inadequate Free-Time Management: A five-day clearance delay costs $750–1,500 in avoidable demurrage and plug-in fees.
Reactive Compliance: Fixing documentation issues after arrival costs exponentially more than pre-shipment preparation.
Peak Season Premiums: Chinese New Year and year-end periods see 20–30% higher reefer-specific costs due to port congestion.
Real-World Example: Frozen Shrimp Clearance Timeline and Costs
Product: Frozen vannamei shrimp (HS 0306.17.00), 10kg cartons
Route: Zhanjiang, China → Los Angeles, USA
Container: 40HC reefer, 26 pallets, 22,000kg net
Incoterm: CIF Los Angeles
Cost Summary
Customs duty on this particular shrimp classification was $0 under applicable trade conditions; ADD/CVD rates vary by exporter and should be verified for each shipment.
Partnering with Experienced Logistics Providers
Managing reefer clearance from China requires precision, real-time monitoring, and regulatory expertise. When coordinating health certificates, pre-arrival filings, and tight delivery windows, an experienced logistics partner prevents costly disruptions.
At Gerudo Logistics, we specialize in cold-chain shipments from China to global destinations. Our teams handle China export documentation, PTI coordination, temperature monitoring, pre-arrival filings across multiple jurisdictions, and destination customs broker relationships. Contact to discuss your cold-chain logistics needs.
Final Workflow Summary: Importer Use-Case SOP
Pre-Production Phase
Verify exporter registration and plant approval for your destination
Classify products accurately (HS codes) and confirm duty rates
Secure import licenses covering your product categories
Review label compliance for destination market
Pre-Shipment Phase
Order PTI and install calibrated temperature data logger
Confirm all certificates (health/veterinary/phytosanitary) are issued correctly
Document set-point, ventilation settings, and loading pattern
File pre-arrival notifications (ISF, FDA Prior Notice, TRACES, etc.) on time
Transit and Arrival Phase
Monitor temperature remotely if logger connectivity available
Prepare entry documents for customs broker before B/L release
Confirm container plug-in immediately upon discharge
Respond immediately to inspection requests
Retrieve data logger report for customs verification
Arrange drayage within free time to avoid demurrage
Post-Clearance Phase
Archive all documentation for audit trail or insurance claims
Review performance metrics (transit time, clearance speed, cost actuals)
Update SOPs based on lessons learned
Frequently Asked Questions for Reefer Customs Clearance
What core documents do I need for a reefer export from China?
Commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, China export declaration, health/veterinary certificate (animal products) or phytosanitary certificate (plant products), certificate of origin, PTI record, and temperature logger report. Add destination-specific pre-notifications.
Which products require a health certificate versus a phytosanitary certificate?
Animal-origin products (meat, seafood, dairy) require health or veterinary certificates. Plant products (fruit, vegetables) require phytosanitary certificates. Some fruits need cold-treatment certificates for certain markets.
What is PTI and why does it matter?
PTI (Pre-Trip Inspection) verifies the reefer container's refrigeration unit, sensors, and controls function correctly before loading. It prevents in-transit failures and provides critical evidence for disputes or insurance claims.
Do I need a temperature data logger?
While not always legally mandated, data loggers are strongly expected by buyers, customs authorities, and insurers. Temperature records are often decisive in resolving quality questions or claims.
What pre-arrival filings are common at destination?
US requires ISF 10+2 and FDA Prior Notice. EU needs TRACES NT (CHED-P for animal products). Middle Eastern countries often require embassy-legalized certificates. Latin America demands advance permits. India and Indonesia require product registration and quarantine approvals.
What causes border holds for reefer shipments?
Missing or incorrect certificates, late pre-notifications, HS misclassification, non-compliant labels, and unexplained temperature excursions trigger most holds.
How should I set temperature, ventilation, and airflow?
Follow commodity guidelines: −18°C for frozen products, 0–4°C for chilled items, varied ranges for fresh produce. Document set-point, ventilation settings, and loading pattern. Incorrect settings damage cargo and raise compliance questions.
Conclusion
Customs clearance for reefer containers from China demands accuracy and timing. The key is preparation: verify registrations before production, gather certificates before loading, file notifications before arrival, and monitor temperature continuously.
Whether importing frozen seafood, fresh produce, or chilled dairy, the principles remain constant: understand your cargo, know the regulations, execute with precision, and maintain temperature integrity throughout.
Ready to streamline your reefer imports from China? Contact Gerudo Logistics for expert cold-chain logistics support tailored to your products and destinations.