Complete Guide to Shipping eBikes from China: Everything You Need to Know Before Shipping
The global eBike market has exploded, reaching an estimated value of $60.8 billion by 2032, and China remains the undisputed manufacturing hub for electric bicycles worldwide. Whether you're an established retailer or an entrepreneur looking to enter the eBike market, understanding how to navigate the complexities of shipping eBikes from China has never been more critical.
Recent developments in 2025 have significantly altered the landscape. With evolving duty structures, updated lithium battery regulations, and shifting trade policies, importing eBikes requires careful planning and expert knowledge. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of eBike shipping from China, ensuring you make informed decisions that protect your business and maximize profitability.
1. Why Is eBike Shipping More Complicated Than Regular Cargo?
The Unique Challenge of eBikes
Shipping eBikes from China presents a perfect storm of logistical challenges that set them apart from virtually any other product category. Unlike standard bicycles or typical consumer electronics, eBikes occupy a unique intersection that creates multiple layers of complexity.
Regulatory Intersection: eBikes straddle multiple regulatory categories simultaneously. They're classified as both transportation vehicles and electronic devices, subjecting them to:
Vehicle safety standards (speed limitations, braking systems)
Electronic device regulations (electromagnetic compatibility)
Battery transportation rules (IATA DGR, UN 38.3)
Import classification complexities (varying HS codes globally)
Physical Shipping Challenges: With weights ranging from 20-35kg and awkward dimensions, eBikes are neither small packages nor standard freight. Their size makes them expensive to ship by air, while their electronic components require careful protection during long sea voyages.
Market Standards Complexity: Different markets have vastly different eBike definitions:
South America: Power limits range from 250W-350W, speed limits 25km/h
Middle East: Generally 250W limit, 20-25km/h, with varying certification requirements
Brazil/Colombia: Higher 350W tolerance compared to other regions
UAE/Qatar: Stricter import permit requirements despite lower duty rates
2. What Makes eBikes a High-Risk Product to Ship?
Breakdown of eBike Components
Main Components and Shipping Implications:
Frame: Standard cargo handling, minimal restrictions
Electric Motor: Electronic device regulations, moderate complexity
Lithium Battery: High-risk dangerous goods, strict regulations
Battery Types: Understanding the Critical Difference
Lead-Acid Batteries:
Classification: Regular cargo
Shipping: Standard freight procedures
Regulations: Minimal restrictions
Cost: Lower shipping costs
Usage: Older eBike models, budget segments
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
Classification: Dangerous Goods
UN Classification: UN3481, Class 9
Shipping: Strict dangerous goods regulations
Cost: Significantly higher shipping costs
Usage: Modern eBikes, premium segments
Battery Classification for Shipping
The Role of the Lithium Battery: UN3481, Class 9 Dangerous Goods
Why Lithium Batteries Create Complexity:
High energy density (400-750Wh typical for eBikes)
Risk of thermal runaway if damaged or overcharged
Strict state-of-charge limitations (30% maximum recommended for 2025)
Special packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements
Limited carrier acceptance, especially for air freight
Regulatory Impact:
IATA dangerous goods regulations for air transport
IMDG code compliance for sea freight
Special training required for handling personnel
Enhanced insurance requirements
Potential for shipment rejection if non-compliant
3. How Much Does It Cost to Ship eBikes from China in 2025?
Shipping costs are just one part of your landed cost and optimization starts with how you plan your route and load.
eBike Shipping Cost Structure
When budgeting for eBike imports, understand that shipping costs represent only one component of your total landed cost. Here's the comprehensive breakdown:
Shipping Method Comparison
Cost Optimization Strategies
Volume Efficiencies:
Full container loads reduce per-unit costs
Consolidated shipments for smaller quantities
Annual shipping contracts for regular importers
Route Optimization:
West Coast vs. East Coast for US imports
Direct vs. transshipment routes
Seasonal rate considerations
Payment Terms:
EXW: Buyer handles all shipping
FOB: Seller delivers to port
CIF: Seller pays freight and insurance
DDP: Seller handles all costs to destination
4. Which Shipping Method Should You Choose: Sea, Air, or Rail?
Sea Freight: The Economic Choice
Best For: Bulk shipments, cost-sensitive cargo, non-urgent deliveries
Container Options:
20ft container: 60-80 eBikes (depending on packaging)
40HQ container: 156-204 eBikes
LCL: For smaller quantities, shared container space
Costs: Approximately 3x higher than pre-2020 levels but still most economical for bulk orders.
Air Freight: Speed at Premium Cost
Best For: Samples, urgent orders, high-value shipments
Transit Times: 3-10 days depending on route and carrier acceptance
Costs: $600+ per eBike to US (varies by weight/dimensions)
Battery Restrictions: Stricter IATA regulations apply; 30% max state of charge recommended.
Rail Freight: The Balanced Option
Best For: China-Europe routes, balanced cost-speed requirements
Transit Times: 15-20 days China to Europe
Advantages:
Lower cost than air freight
Faster than sea freight
More environmentally sustainable
Reduced port congestion issues
5. What Documents Do You Need for eBike Shipping?
Mandatory Documentation for All Shipments:
Commercial invoice with detailed product specifications
Packing list including battery specifications
Certificate of origin
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for batteries
Shipper's Declaration for Dangerous Goods (DGD)
Air Freight Additional:
IATA Lithium Battery Handling Label
Pilot notification (NOTOC)
State of charge documentation
Sea/Rail Freight Additional:
IMDG dangerous goods declaration
Container loading certificate
VGM (Verified Gross Mass) declaration
6. Understanding eBike Transportation Risks
Critical Risk Factors in eBike Shipping
Shipping eBikes involves unique risks that go beyond typical cargo concerns. The combination of electronic components, lithium batteries, and mechanical parts creates multiple risk vectors that require careful management.
Battery-Related Risks:
Thermal Runaway: Overheating, fire, or explosion from damage or overcharging.
Electrolyte Leakage: Corrosive leaks damaging cargo and posing environmental hazards.
Gas Emission: Toxic gas release requiring special ventilation.
Short Circuit Risk: Electrical shorts from damaged terminals, causing fire hazards.
Physical and Environmental Risks:
Moisture Damage: Risk of water damage during sea transport.
Vibration and Impact: Potential damage from handling and movement.
Temperature Extremes: Affecting battery and component performance.
Electromagnetic Interference: Packaging failure causing interference with electronics.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks:
Shipment Rejection: Delays or rejections for non-compliance.
Port Delays: Extended inspections and fees due to poor documentation.
Insurance Voids: Non-compliance can void coverage.
Legal Liability: Legal and financial consequences from improper shipping.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
Implement robust packaging protocols with proper cushioning and moisture protection
Ensure batteries are shipped at recommended 30% state of charge
Use certified dangerous goods packaging and labeling
Work with carriers experienced in lithium battery transportation
Maintain comprehensive insurance coverage including dangerous goods riders
Establish emergency response procedures for battery-related incidents
7. Should You Ship eBikes With or Without Batteries?
The Battery Separation Decision Matrix
Ship Complete eBikes When:
Volume Justifies Complexity: Large container loads where dangerous goods procedures are worthwhile
No Local Battery Source: Target market lacks reliable battery suppliers
Customer Preference: End customers expect complete, ready-to-use products
Cost Analysis Favors: Total landed cost is competitive despite shipping complexity
Ship Without Batteries When:
Regulatory Simplification: Avoid dangerous goods procedures and restrictions
Cost Optimization: Significant savings on shipping and handling fees
Local Assembly Capability: You have local technical support for battery installation
Market Testing: Initial market entry with simplified logistics
Separate Battery Shipping Considerations
Advantages of Battery Separation:
Eliminates dangerous goods restrictions for the eBike frame
Reduces shipping costs by 20-40%
Allows use of more carriers and shipping methods
Simplifies customs clearance procedures
Challenges of Battery Separation:
Requires two separate shipments and logistics coordination
Local battery sourcing may have quality concerns
Installation and warranty complexity
Potential customer dissatisfaction with incomplete products
Local Battery Sourcing vs. Separate Shipping
Local Sourcing Evaluation Criteria:
Quality Standards: Can local suppliers meet your specifications?
Cost Competitiveness: Total cost including procurement, testing, and warranty
Supply Reliability: Consistent availability and delivery performance
Compliance: Local suppliers' certification and regulatory compliance
8. How Do Tariffs and Duties Affect eBike Imports in 2025?
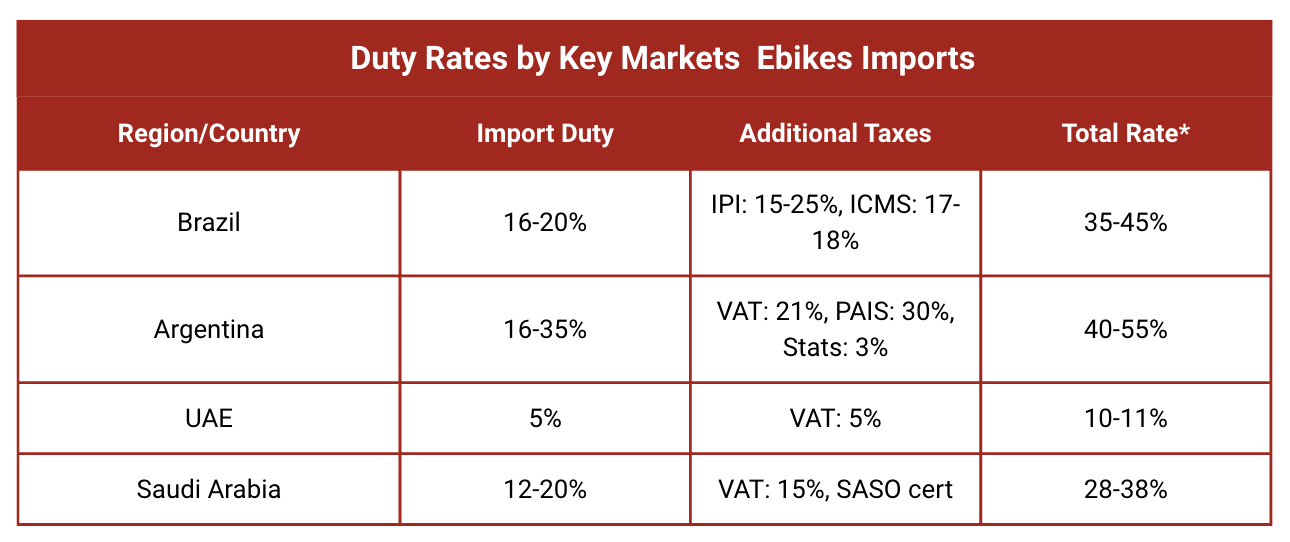
Import duties can easily add 30–50% to your landed cost depending on destination, here’s how the major markets compare:
Duty Rates by Key Markets
*Total effective rate on CIF value including all applicable taxes
Strategic Market Implications
High-Duty Markets (South America):
Require premium positioning or volume economies
Focus on differentiated, high-value products
Consider local assembly to reduce duty burden
Low-Duty Markets (Middle East):
Allow competitive pricing strategies
Enable faster market penetration
Suitable for market testing and expansion
Duty Optimization Strategies
HS Code Optimization: Work with customs experts to ensure most favorable classification
Value Engineering: Consider component separation for different duty rates
Free Trade Agreements: Explore alternative sourcing countries with preferential rates
9. Choose the Right Freight Forwarder for eBikes
At Gerudo Logistics, we understand that eBike importers need more than basic freight forwarding, you need specialized expertise and strategic partnership. Our proven track record in eBike shipping from China includes extensive experience with lithium battery regulations, market-specific certifications, and the complex requirements of South American and Middle Eastern markets.
Why eBike Importers Choose Gerudo:
Specialized Expertise: Dedicated dangerous goods certification and eBike shipping experience
Market Knowledge: Deep understanding of INMETRO (Brazil), SASO (Saudi Arabia), and other regional requirements
Transparent Pricing: All-inclusive quotes with no hidden fees for dangerous goods handling
Strategic Support: Route optimization, packaging consultation, and risk management guidance
We don't just move your cargo – we're invested in optimizing your total landed costs and ensuring compliance across all your target markets. Our comprehensive service includes everything from supplier pickup in China to final delivery at your warehouse, with proactive communication throughout the entire process.
10. Conclusion
Shipping eBikes from China in 2025 isn't just about moving cargo, it's about managing compliance, cost, and risk.
Lithium batteries classified under UN3481 Class 9 Dangerous Goods make eBike logistics far more complex than standard freight, requiring strict adherence to documentation, packaging, and transport rules.
Success depends on choosing the right strategy, whether shipping complete eBikes or separating batteries, and understanding how tariffs, certifications, and regulations impact your total landed cost.
Ready to navigate the complexities of eBike importing? Contact experienced dangerous goods specialists who can help you develop a comprehensive strategy that addresses your specific market requirements while optimizing costs and ensuring full regulatory compliance throughout the process.